 |
|
|
|
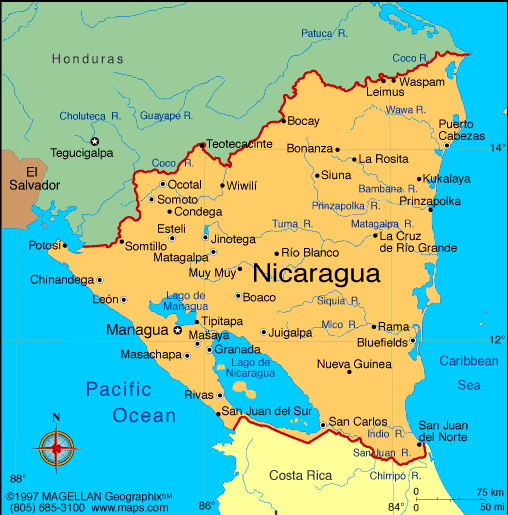
Nicaragua
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Background: The Pacific Coast of Nicaragua was
settled as a Spanish colony from Panama in the early 16th century. Independence
from Spain was declared in 1821 and the country became an independent
republic in 1838. Britain occupied the Caribbean Coast in the first half
of the 19th century, but gradually ceded control of the region in subsequent
decades. Violent opposition to governmental manipulation and corruption
spread to all classes by 1978 and resulted in a short-lived civil war
that brought the Marxist Sandinista guerrillas to power in 1979. Nicaraguan
aid to leftist rebels in El Salvador caused the US to sponsor anti-Sandinista
contra guerrillas through much of the 1980s. Free elections in 1990, 1996,
and again in 2001 saw the Sandinistas defeated. The country has slowly
rebuilt its economy during the 1990s, but was hard hit by Hurricane Mitch
in 1998.
|
|
|
|
Geography |
|
|
|
Location: Central America,
bordering both the Caribbean Sea and the North Pacific Ocean, between Costa
Rica and Honduras |
|
|
|
Area: total: 129,494 sq
km
water: 9,240 sq km
land: 120,254 sq km |
|
|
|
Climate: tropical in lowlands,
cooler in highlands |
|
|
|
Terrain: extensive Atlantic
coastal plains rising to central interior mountains; narrow Pacific coastal
plain interrupted by volcanoes |
|
|
|
People |
|
|
|
Population: 5,359,759 (July
2004 est.) |
|
|
|
Population growth rate:
1.97% (2004 est.) |
|
|
|
Languages: Spanish (official)
note: English and indigenous languages on Atlantic coast |
|
|
|
Government |
|
|
|
Country name:
conventional long form: Republic of Nicaragua
conventional short form: Nicaragua
local short form: Nicaragua
local long form: Republica de Nicaragua |
|
|
|
Government type: republic
|
|
|
|
Capital:
Managua |
|
|
|
Administrative divisions:
15 departments (departamentos, singular - departamento) and 2 autonomous
regions* (regiones autonomistas, singular - region autonomista); Atlantico
Norte*, Atlantico Sur*, Boaco, Carazo, Chinandega, Chontales, Esteli, Granada,
Jinotega, Leon, Madriz, Managua, Masaya, Matagalpa, Nueva Segovia, Rio San
Juan, Rivas |
|
|
|
Independence: 15 September
1821 (from Spain) |
|
|
|
National holiday: Independence
Day, 15 September (1821) |
|
|
|
chief of state: President
Enrique BOLANOS Geyer (since 10 January 2002); Vice President Jose RIZO
Castellon (since 10 January 2002); note - the president is both chief of
state and head of government |
|
|
|
Economy |
|
|
|
overview: Nicaragua,
one of the hemisphere's poorest countries, faces low per capita income,
massive unemployment, and huge external debt. Distribution of income is
one of the most unequal on the globe. While the country has made progress
toward macroeconomic stability over the past few years, GDP annual growth
of 1.5% - 2.5% has been far too low to meet the country's need. Nicaragua
will continue to be dependent on international aid and debt relief under
the Heavily Indebted Poor Countries (HIPC) initiative. Nicaragua has undertaken
significant economic reforms that are expected to help the country qualify
for more than $4 billion in debt relief under HIPC in early 2004. Donors
have made aid conditional on the openness of government financial operation,
poverty alleviation, and human rights. A three-year poverty reduction and
growth plan, agreed to with the IMF in December 2002, guides economic policy.
|
|
|
|
GDP:
purchasing power parity - $11.49 billion (2003 est.)
GDP - real growth rate: 1.4% (2003 est.)
GDP - per capita: purchasing power parity - $2,200 (2003 est.)
GDP - composition by sector: agriculture: 30.5%; industry: 22.5%;
services: 47% (2002 est.) |
|
|
|
Currency: gold
cordoba (NIO) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| back |
|
|
|
|

